Data transformations are often the most complex and costly part of an ETL and ELT process. They can vary from simple data conversions to extremely complex data aggregating techniques. Enterprises use data warehouses to accumulate data from multiple sources for data analysis and research.
CData Sync not only offers a robust replication mechanism tailored to efficiently transfer data into your SQL Server environment from any of the 250+ supported SaaS, Big Data, and NoSQL sources but also enables you to transform the data on the go.
In this article, we will briefly describe how to replicate multiples tables from a data source into SQL Server and then transform those datasets with the JOIN clause, a technique extensively employed across various industries to analyze their data, using CData Sync. We will use Salesforce as a data source to extract the datasets, but the principles apply to any of our 250+ supported sources.
For a detailed guide on Data Transformation and a better understanding of this use case, check out our in-depth documentation.
1. Replicate tables from a data source to SQL Server
Always-on applications rely on automatic failover capabilities and real-time data access. CData Sync integrates live Salesforce data into your SQL Server instance, allowing you to consolidate all of your data into a single location for archiving, reporting, analytics, machine learning, artificial intelligence and more.
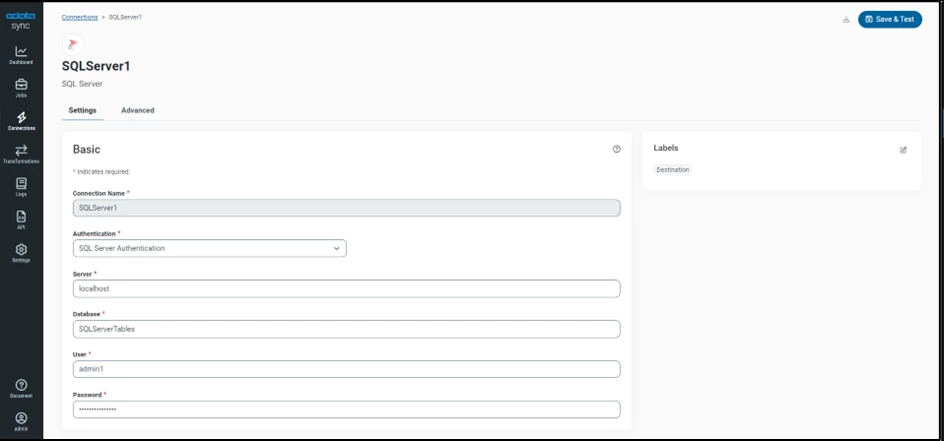
a. Configure SQL Server as a Replication Destination
Using CData Sync, you can replicate Salesforce data to SQL Server. To add a replication destination, navigate to the Connections tab.
- Click on Add Connection.
- Select the Destinations tab.
- Search and select a database (SQL Server).
- Configure the connection properties.
b. Configure the data source connection
You can configure a connection to Salesforce from the Connections tab. To add a connection to your Salesforce account, navigate to the Connections tab.
- Click on Add Connection.
- Select the Sources tab.
- Select a data source (Salesforce)
- Configure the connection properties.
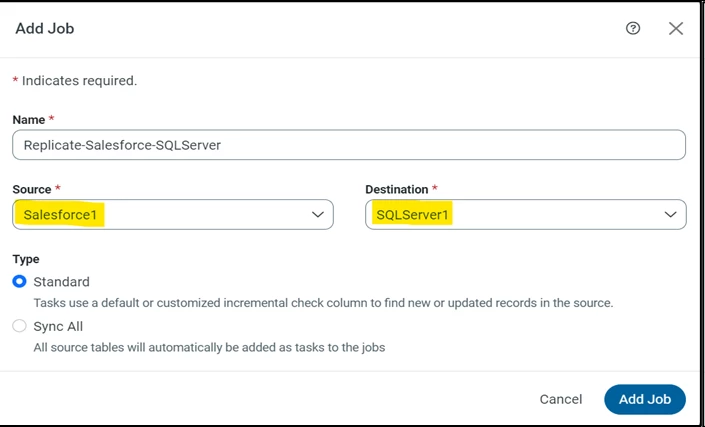
c. Configure Replication Tasks
CData Sync enables you to control replication with a point-and-click interface and with SQL queries. For each replication you wish to configure, navigate to the Jobs tab, and click Add Job. Select the Source and Destination for your replication.
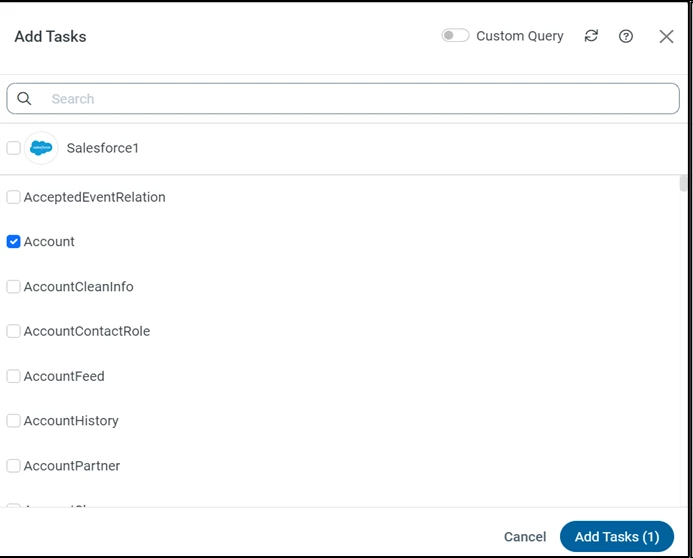
i. Replicate Entire Tables
To replicate an entire table, click Add Tasks in the Task section, choose the table(s) you wish to replicate, and click Add Tasks.
ii. Customize Your Replication
You can use the Columns and Query tabs of a task to customize your replication. The Columns tab allows you to specify which columns to replicate, rename the columns at the destination, and even perform operations on the source data before replicating. The Query tab allows you to add filters, grouping, and sorting to the replication.
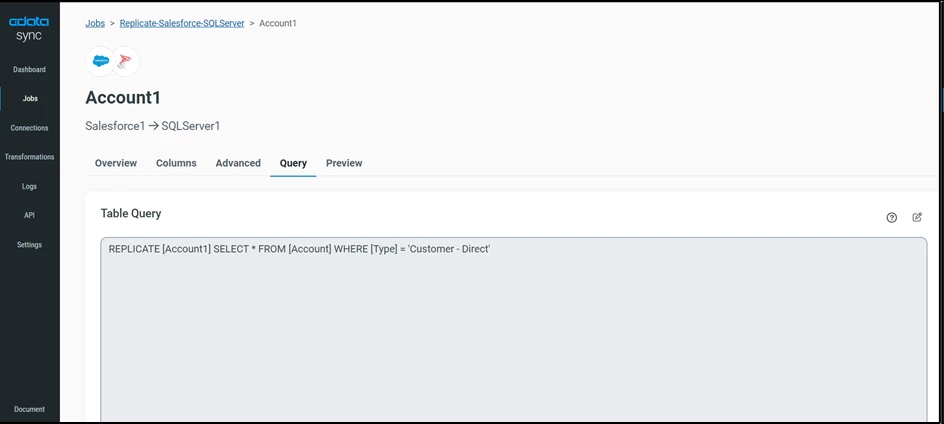
You can also utilize a newly introduced feature called 'Custom Query,' allowing you to make on-the-go customization while adding a new task in CData Sync.

2. Transformation post-replication: Destination Transformation
After you have replicated the required datasets from your data source, proceed to the Transformation tab and select Add Transformations to create a transformation job. In this section, we will delve into a couple of methods for utilizing the JOIN query, as it represents one of the most widely applied transformations across industries for generating daily reports, analyzing critical data and building new applications.
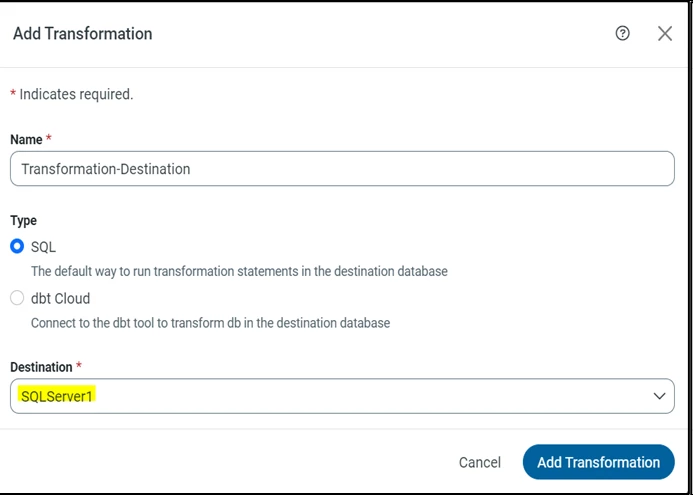
Add a SQL transformation query
This type of transformation processes external SQL scripts or SQL queries that you create in an SQL editor. You can use these queries to insert, delete, update, and retrieve rows from a database. The SQL transformation processes the queries, returning rows and database errors. After creating a transformation job, add custom queries in the Query.
For a detailed guide on Post-Job (ELT) Transformations using CData Sync, check out our in-depth documentation.
a. INNER JOIN
An INNER JOIN query in SQL is used to combine rows from two or more tables based on a related column between them. It returns only the rows where there is a match in both tables, effectively filtering out rows that do not have corresponding values in the specified columns.
SELECT
[Account1].[Id],
[Account1].[Name],
[Account1].[Fax],
[Opportunity1].[AccountId],
[Opportunity1].[CloseDate]
INTO
Inner_Joined_Table
FROM
[Account1]
INNER JOIN [Opportunity1]
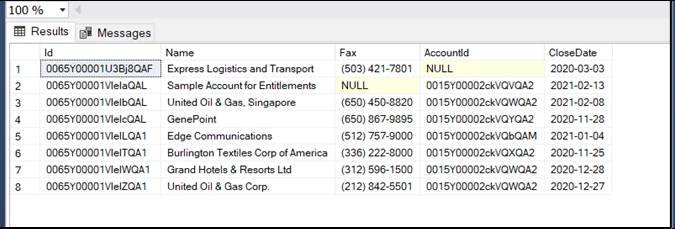
ON [Account1].[Id] = [Opportunity1].[Id]; RESULT (SQL SERVER):
b. LEFT JOIN:
A LEFT JOIN (or LEFT OUTER JOIN) query in SQL is used to retrieve all records from the left table (table1) and the matched records from the right table (table2). If there is no match found in the right table, NULL values are returned for columns from the right table.
SELECT
[Contact1].[FirstName],
[Account1].[Name]
INTO
Left_Joined_Table
FROM
[Account1]
LEFT JOIN [Contact1]
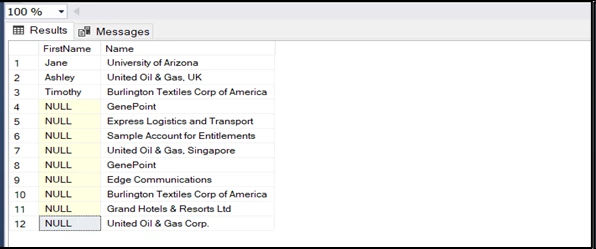
ON [Account1].[Id] = [Contact1].[AccountId] RESULT (SQL SERVER):
Business Use Cases
Some possible business use cases utilizing transformations post-replication jobs are:
- A retail company can employ replication to transfer sales data from its point-of-sale systems to a central data warehouse. Subsequently, the company can utilize transformations to clean and normalize the data in the data warehouse.
- A financial company has the option to utilize replication for duplicating customer account data from its core banking system to a data warehouse. Following this, the company can employ transformations to filter the data, including only customers with a specific balance or those who have been inactive for a certain period of time.
- A healthcare provider has the capability to apply replication for duplicating patient data from its electronic health record system to a data warehouse. The company can then employ transformations to aggregate the data, enabling the creation of reports on disease prevalence or treatment effectiveness.
More information & free trial
Now that you have seen how to replicate and transform your source data in SQL Server using CData Sync, visit our CData Sync page to read more information about CData Sync and download a 30-day free trial. As always, our world-class Support Team is ready to answer any questions you may have!


